
In recent years diabetes has become a prevalent problem, and some even go so far as to call it an epidemic. The number of people being diagnosed with this disease is rising worldwide. In the US alone there are an estimated 29.1 million people with diabetes.
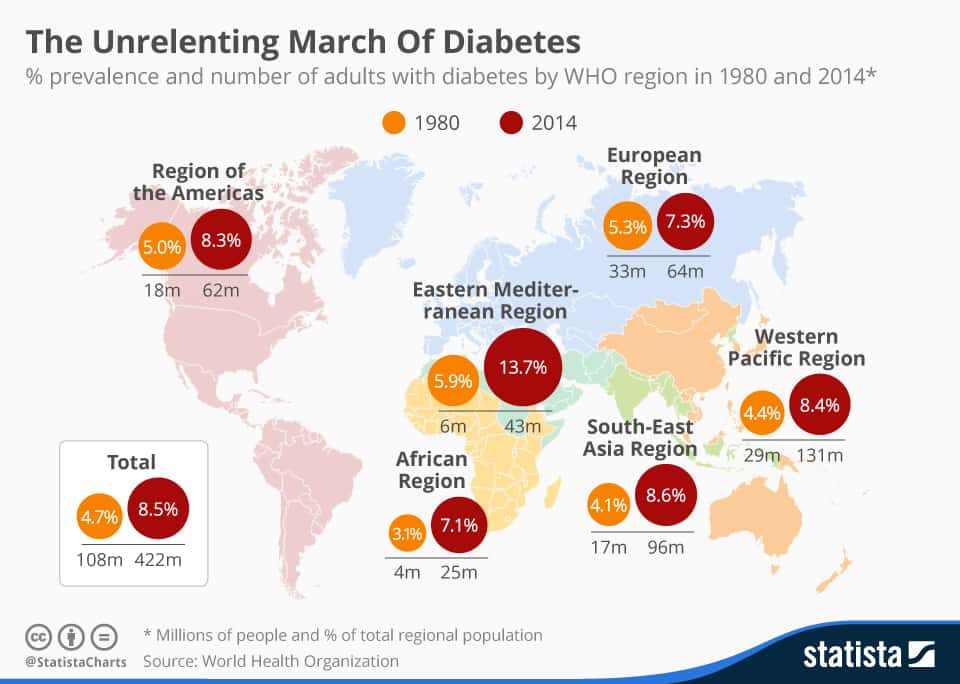
Of these 8.1 million are cases of people who are un-diagnosed. Diabetes is the world's eighth biggest killer, accounting for some 1.5 million deaths each year, according to Statista. A new report from the World Health Organization reveals that the number of cases worldwide has nearly quadrupled to 422 million in 2014 from 108 million in 1980.
According to statistics gathered by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), 37% of adults over the age of 20 in the US had pre-diabetes in 2009-2012.
Because of this ride in the disease it is more important than ever for people to be educated about diabetes.
It is a serious chronic condition that can be treated with medication, and sometimes managed through diet. Many questions come to mind when someone begins to seek information on diabetes.
Here we will try to answer these questions and explore this disease, it's signs, treatments and management.
The definition of diabetes is a disease where the body does not produce enough insulin. Due to this the amount of blood glucose (sugar) in the body can not be controlled as normal. (10) You may have also heard of it called diabetes mellitus.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
There are different types of diabetes, and all these types are categorized as diabetes mellitus.
It is a group of metabolic diseases that due to faulty secretion of insulin, insulin activity or a combination of both leads to hyperglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is when the glucose level in the blood stream is higher than is normal. The most common types of diabetes are Type 1, Type 2 and gestational. (2)
Type 1 Diabetes
In the past Type 1 was known as juvenile onset or insulin dependent diabetes. In this form the pancreas does not produce insulin, which the body uses to convert the glucose from food into energy.
When this conversion does not occur it causes the bloodstream to collect an excess amount of glucose.
Type 1 diabetes can be diagnosed at any age, however it does occur most usually in children and young adults. (3)
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, also known as no insulin dependent or adult onset diabetes most often occurs in middle aged or older adult, however more and more of it is appearing in younger people who are overweight.
This category of diabetes mellitus is chronic., and glucose is metabolized by the body affected by it.
Type 2 causes either the pancreas to not produce sufficient amounts of insulin or your body does not produce insulin correctly. In both instances your body can not properly regulate it’s glucose levels. (8)
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes, like other types, affects how the body processes glucose. It occurs during pregnancy, and most usually goes away after the birth. However once a women has had this type they become at risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. (2)
It is very treatable, it can be controlled with diet, exercise and sometimes medication. Most pregnant women do not show signs of gestational diabetes. Screening for it is part of regular prenatal care.
How do You Get Diabetes?
Answering this question is not a simple matter. There is no known exact explanation for how or why people develop diabetes.
Some believe it is due to environmental and genetic factors, and there also seems to be a link between Type 2 and being overweight. However it is not a certainty, people who develop diabetes can be any weight.
Is Diabetes Hereditary?
This too is not simply answered. According to the American Diabetes Association there is not an easily discernible pattern to how diabetes is inherited, yet those who are more likely to develop the disease are from birth.
The causes of Type 1 and Type 2 are different, but both can depend on whether there is a inherited disposition to diabetes.
Even with the disease in a person’s background it is not an absolute conclusion they will end up being diabetic.
An environmental trigger is also an important factor in whether or not an individual will develop diabetes.
Ongoing research is attempting to discover what these triggers may be. Diet and lifestyle have been found to have an influence over the development of Type 2 diabetes along with genetic and other environmental factors . (7)
So, if there is no clear cut easy answer as to how and why someone ends up becoming diabetic, you may ask yourself can it be prevented?
How to Avoid Diabetes?
According to George King of the Joslin Center for Diabetes, one of the leading authorities in the treatment and research of the disease, says in his book The Diabetes Reset,
...you can always take steps to improve your body’s response to insulin and ‘reset’ your ability to metabolize the glucose in your blood.
King also researched and organized a plan he says will help avoid, control and even reverse diabetes. It is well known that many cases of Type 2 can be managed through dietary changes.
The Joslin Diabetes Center has shown through research that a diet low in fat and high in fiber can improve your risk of Type 2 diabetes, sensitivity to insulin and how glucose is metabolized.
According to King and the Joslin Center this improvement is based on a specific diet plan that consists of 15% each of protein and fat, 70% carbohydrates and 15 grams of fiber per 1000 calories a person consumes.
There has been research which also links diet and lifestyle changes to successfully preventing and managing Type 2 diabetes.
Now that we have a better overall understanding of diabetes the next question is,
What are the Signs of Diabetes?
The early signs of diabetes can be very subtle. There is also the possibility that an individual will not experience any symptoms at all. However serious complications can still develop even without symptoms.
Women and men in general manifest similar early symptoms of diabetes. These common warnings can include fatigue, weight loss, headaches, blurry vision, dry mouth, an increase in hunger and thirst as well as higher frequency of urination or infections. (11)
Although these are common in both sexes there are some signs of diabetes in men that could be more visible or only experienced by men.
Some of these male specific symptoms are erectile dysfunction, a loss due to muscle mass reduction, itching or recurring cases of thrush around the penile area. (2)
Even though most people who develop diabetes are adults there seems to be an increase in the numbers of children with diabetes.
The signs of diabetes in children are similar to those of adults such as weight loss, fatigue and an increase of urination and thirst.
Once you have experienced any of the common symptoms you might begin to wonder, "do I have diabetes?"
Determining whether you may have diabetes is not as simple as waking up one morning and suddenly realizing you have to urinate a lot and you're so thirsty and hungry all the time.
The symptoms don't just hit all at once, they can slowly develop over time, and go on unnoticed for years.
So if these signs can be so subtle, you are probably asking "how do I know"? Talking to your physician when you have any reason to believe you may have the disease is the first step.
How to Tell if You Have Diabetes?
There are a few ways to screen for diabetes, and even if you have not noticed any warning signs of the disease certain people are recommended by the American Diabetes Association to be tests.
No matter how old you are if your body mass is over 25, and you also have high cholesterol or blood pressure, history of gestational diabetes, heart disease or diabetic relatives you should be tested.
It is also suggested that people over the age of 45 should be screened on a regular basis. (3) The only way to know positively if you have diabetes is to be tested.
There are a variety of tests that can determine whether you are pre-diabetic, diabetic or neither.
How to Test for Diabetes?
The most common test for pre-diabetes, Type 1 and Type 2 is the A1C test. It is a blood test administered by a doctor which measures your average glucose level in your blood over the past 2 to 3 months.
At certain times your doctor may decide using a different test is required, in this instance a fasting blood sugar test, random blood sugar test or oral glucose tolerance test can be an option for diagnosing diabetes.
Blood glucose levels can also be tested at home with testing kits such as the Bayer Contour NEXT EZ Meter, the TrueResult Meter or ACCUCHEK Aviva Blood Glucose Meter.
Machines like these can be used to monitor and keep track of your blood glucose levels throughout the day. They are not recommended to be used as a replacement for a physician’s diagnosis.
These monitors are easily operated to quickly produce accurate readings of your blood sugar levels.
Once you have been tested and diagnosed with diabetes it is important to know which foods to eat. Whether or not taking insulin is part of your treatment, your diet is a major factor in successfully managing the disease.
So, What can Diabetics Eat?
The best foods for diabetics assist your body with controlling glucose levels in your blood. When planning meals for diabetics it is important to include mono-saturated and polysaturated fats, foods high in fiber, healthy carbohydrates and fish.
The Mayo Clinic Diet, a New York bestseller, uses a variety of these types of foods to create a whole place signed to help with weight loss and blood sugar control.
Another source for meal plans and recipes for diabetics is What Do I Eat Now A Step by Step Guide to Eating Right With Type 2 Diabetes by Tami Ross and Patti Geil.
There is no reason that having diabetes should prevent you from enjoying good food. There are numerous healthy and tasty possible dishes for dinner, lunch and breakfast for diabetics.
Just remember to stick to the right foods. It is really quite easy to create a meal plan that will help you maintain or even prevent diabetes. There are many books and guides available which can take all the guess work out of developing your new diabetic diet.
Not only are these diets good for those who have pre-diabetes, Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, most are just plain good for you. These diets help you lose any excess pounds and maintain a healthy weight.
There is a plethora of programs which aid you in meal planning using different methods. Some contain more detailed and complex plans while others offer smaller, easier methods. It is all up to your preference.
Portion control has long been a recommended way to control your food intake for a healthier diet. It can also be a great way to help diabetics eat right.
An example of this type of program is called Diabetic Meals by the Plate by the editors of Diabetic Living magazine. This simple program utilizes portion control along with low carb recipes to design an easy to follow diet. (13)
Eating as a diabetic does not have to be a difficult undertaking, with a little information and help anyone can enjoy food without a lot of work or fuss.
Although this disease should be taken seriously it does not have to be a great burden. Nevertheless, you might want to know if there is a cure.
Can Diabetes be Cured?
Unfortunately the answer is no. This is a chronic condition that will not go away. Although there is no cure for diabetes it is very easily treatable and in some cases preventable.
As stated earlier it can be managed with diet and when necessary with medication. Diabetes can however cause a strain on your body and health.
Sometimes vitamins and minerals can be very beneficial to your treatment regimen.
Vitamins and minerals are important to how your body metabolizes glucose, and it is recommended that the majority of diabetics take daily doses to supplement what they should be receiving through food and other natural sources. (6)
According to the Joslin Diabetes Center it is recommended that you should try to mostly get the nutrients you need by eating foods that provide a variety of different vitamins and minerals.
However, they do suggest that supplements are a good choice for those who follow low calorie or vegan diets, pregnant women and those who just do not eat an array of foods.
One vitamin which Dr. Nora Saul, a patient educator at the Joslin Clinic emphasizes as a need for all people not just diabetics is Vitamin D.
If for any reason you suspect you are not receiving the proper nutrients through your diet, a vitamin supplement is a good option. (10)
There is a wide range of supplements designed specifically with the needs of diabetics in mind.
A good examples of which is Nature Made’s Diabetes Health Pack that has been formulated to provide the best nutritional benefits for people with diabetes.
Over the years there has been a lot of controversy surrounding diabetes. So called miracle cures have promised that a certain pill, powder or program would completely eradicate the disease, and then there are the doctors and researchers who are constantly debating the best treatment methods, causes, pre-diabetes classification and over screening.
So many differences in opinion and the fake cures make it difficult to determine what to believe when new information comes to light. Especially when it comes to news of a new way to cure or reverse the disease.
However with the new scientific studies and research, it is beginning to look as if some of the promises made by the treatments and programs could be true.
Even the most unbelievable sounding, like the 100 year old vaccine that could be used to reverse Type 1 diabetes. (9)
In June 2015 a new human trial was announced which will test and study bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) on adults between the ages of 18 and 60 who have Type 1 diabetes.
BCG isn't new; it has been used for 100 years as a tuberculosis vaccine as well as more recently as a treatment for bladder cancer.
This study is actually a phase II trial as it has already successfully reversed Type 1 in mice and in 103 humans during phase 1.
The study has already shown BCG temporarily destroying the abnormal cells that cause diabetes.
It was also able to allow for a slight rise in insulin production. This BCG trial is unusual because instead of focusing on newer diabetics like most research, this trial is concentrated on Type 1 diabetics who have been diagnosed for many years.
Although it will be at least 5 more years before the final results will be known, the early evidence is positive and hopeful.
While the reversing of Type 1 diabetes is a viable possibility in the future, what about Type 2? What about right now?
What About Reversing Diabetes?
What does it mean to reverse diabetes? The most common understanding is it is a reversing of the disease’s progression, essentially a remission.
While the illness and it's possible recurrence doesn't just vanish, a remission of Type 2 diabetes produces blood glucose levels that lower to normal or pre-diabetes levels.
There has been much research done to determine if Type 2 diabetes is reversible.
One of these studies was published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) in December 2012.
Dr. Monika Safford, co-author of the study has said that because Type 2 is heavily associated with lifestyle, reversing it is a plausible concept.
Dr. Safford was correct, it is not only a plausible idea, but it is actually possible.This study showed that major diet and lifestyle changes resulted in some of the participants experiencing a remission in their diabetes.
There were even cases where the need of diabetes maintenance medication was eliminated. (11)
The ability to reverse or manage diabetes naturally without using medication is extremely desirable for many people.
However, using a program that has the potential of reversing it through changes in lifestyle and diet is a long term undertaking. To maintain a remission the changes must be permanent or a recurrence is inevitable.
Yet more evidence that an alternative diet and lifestyle could assist in reversing the disease has been shown through a clinical trial which was published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition on April 1, 2009.
In this trial Dr. Neal D. Barnard and associates studied the effects of a low-fat vegan diet on blood glucose, weight and cholesterol levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes. (1)
This study showed blood glucose improvements and weight loss both of which have been found to be major factors in diabetes prevention and reversal.
There was also a marked decrease in total cholesterol.
Using information gathered from studies such as this one, Dr. Barnard developed a system for reversing it by controlling glucose levels and repairing insulin function while increasing overall health.
This system has been compiled in the book, Dr. Neal Barnard’s Program for Reversing Diabetes: The Scientifically Proven System for Reversing Diabetes without Drugs.
Another example of these natural diabetes prevention and reversal programs created is The End of Diabetes: The Eat to Live Plan to Prevent and Reverse Diabetes by Dr. Joel Fuhrman M.D. Dr. Fuhrman works with the Nutritional Research Foundation as the director of research, and has authored 7 other nutritional based diet books.
He has also been published in scientific journals such as the Nutrition Journal and the Open Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Diabetes mellitus is a serious illness which left untreated can lead to life threatening complications, however with the proper care it can be easily managed, and in certain cases prevented or even reversed.
Becoming educated about diabetes is the first step in the journey. Hopefully this information has helped your understanding of the subject.
Copyright text 2020 by 5MinuteReviews.com
Important Disclaimer: The information contained on 5MinuteReviews.com is intended for informational and educational purposes only. 5MinuteReviews.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to 5MinuteReviews.com.

Disclaimer: The information contained within this site is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have, expect to have, or suspect you may have any medical condition, you are urged to consult with a health care provider. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any diseases or medical conditions. Results are based on 5MinuteReviews.com Ranking System and do not necessarily reflect typical results from the use of these products. Please visit product websites for more information.
FTC Disclosure: We represent a professional research and review team, and on our page you may find affiliate links for which we could be compensated for by clicking on them. https://5MinuteReviews.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com.
All logos and names are respective to each company and brand, all registered trademarks and protected images are used under the terms of 'fair use'. Please reach out, we're human too.
